2025-10-20
Seniors and Debt
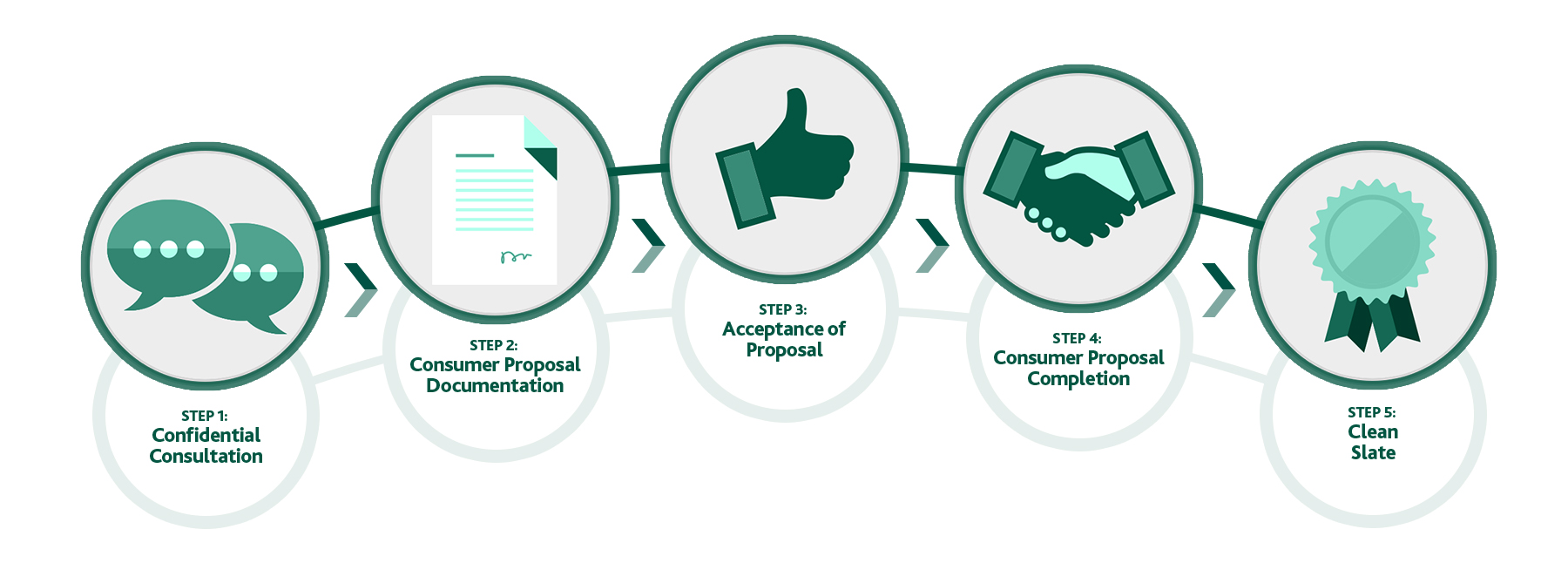
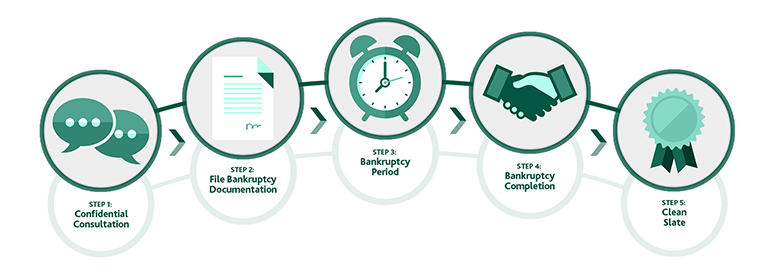
Alternatives to Bankruptcy Bankruptcy Consumer Proposal Lifestyle Debt MNP Consumer Debt Index
Just when seniors should be relaxing and enjoying the fruits of their labour, many find themselves struggling financially — an unsettling contrast to the ease they’d hoped to live their golden years.